Empowering Healthcare Heroes: A Comprehensive Training Program on Snakebite Management
In the heart of Nepal, where agriculture thrives and nature's creatures roam freely, there lies a silent menace: snakebites. The picturesque landscape of Nepal, with its hot climate and abundant rainfall, provides an ideal habitat for snakes. Unfortunately, this coexistence has led to a significant public health issue, impacting the lives of farmers, plantation workers, herdsmen, and fishermen – the backbone of the nation.
Traditional beliefs, lack of awareness, and delays in seeking medical treatment have resulted in tragic consequences, with thousands falling victim to snakebites every year. In the face of this challenge, a beacon of hope emerged through a transformative initiative: the Snakebite Management Training program.
According to the World Health Organization, snakebite is one of the 20 neglected tropical diseases, a term that underscores the urgency of addressing this issue. In Nepal, snakebite-related deaths have been steadily rising due to delayed identification and insufficient healthcare resources. The lack of trained health workers at the community level compounds the problem, often resulting in fatal outcomes.
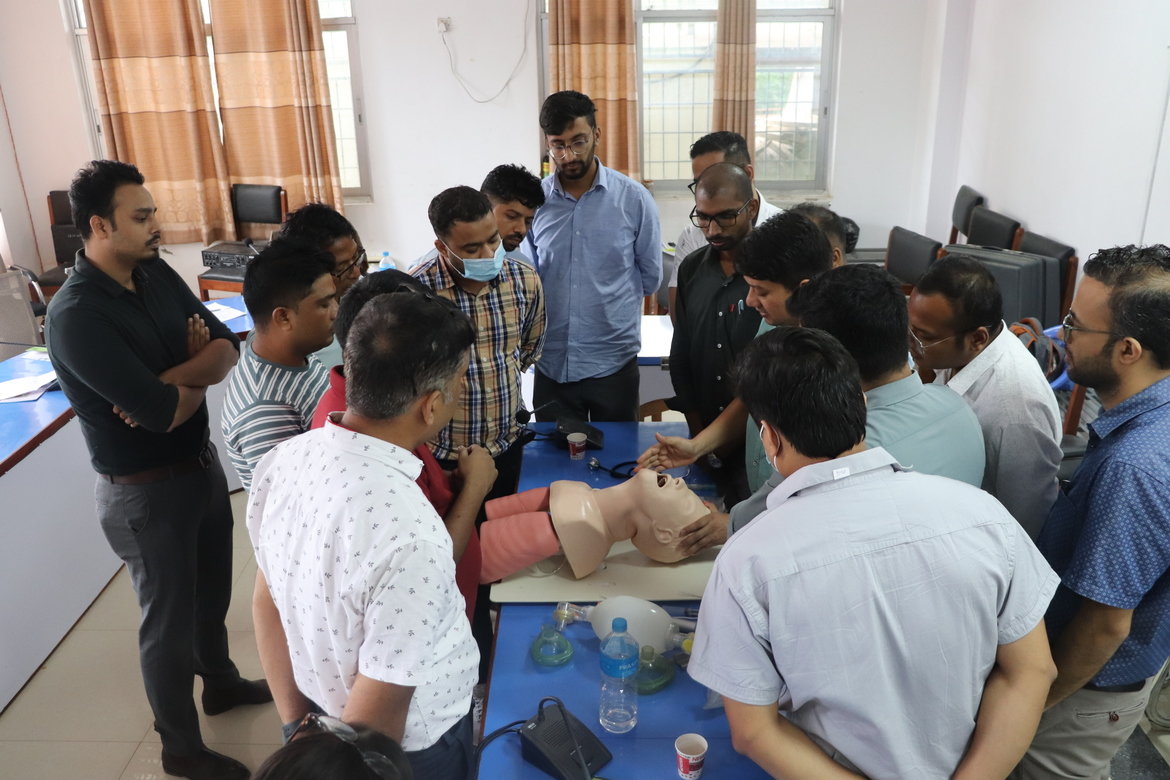
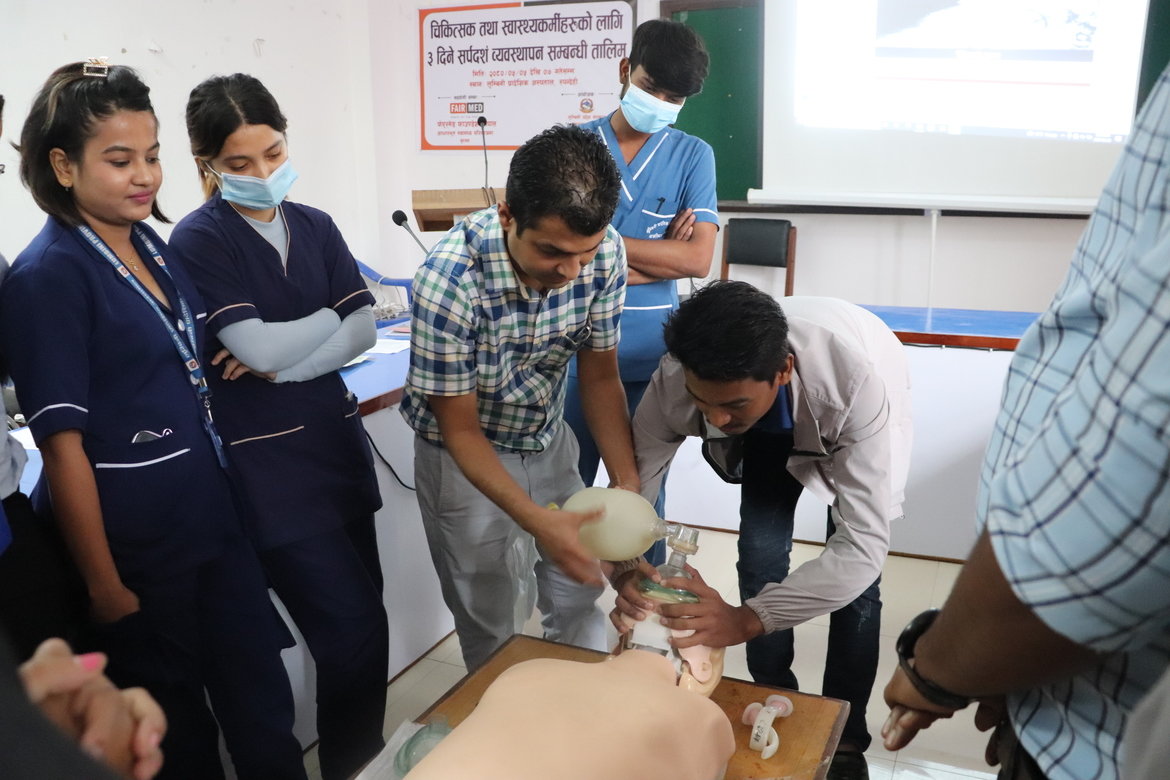
Recognizing the gravity of the situation, FAIRMED Foundation Nepal is actively working with a mission to bridge the gap in snakebite management through empowering healthcare workers. With FAIRMED's support, a three-day training program was conducted in collaboration with the Health Training Center at Lumbini Provincial Hospital. This initiative aimed to equip medical officers, paramedics, and nurses with the necessary skills to handle snakebite cases efficiently and effectively.
The training program had clear objectives, each designed to empower healthcare providers and enhance their capabilities on:
- Differentiating Venomous and Non-Venomous Snakes where participants learned to identify various snake species in Nepal, understanding the key differences between venomous and non-venomous snakes.
- Differentiating Venomous and Non-Venomous Snakes where participants learned to identify various snake species in Nepal, understanding the key differences between venomous and non-venomous snakes.
- First Aid and Immediate Care where essential first aid techniques after snakebites were emphasized, focusing on immobilization, rapid transport to healthcare facilities, and reassurance of the victim.
- Clinical Assessment and Resuscitation where the ABCDE approach (Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, Exposure) was emphasized, ensuring a systematic approach to snakebite cases, along with cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) training.
- Antivenom Treatment and Supportive Care where participants were educated on the timely administration of antivenom and the importance of supportive measures, including airway management and pain relief.
- Role of Health Centers where health posts and primary health centers were highlighted as crucial hubs for snakebite management. Training focused on enhancing the ability of local healthcare providers to manage snakebite cases promptly
The training sessions were conducted using participatory methods, blending lectures with practical demonstrations, group work, and interactive discussions. Experienced trainers from various hospitals shared their expertise, ensuring a comprehensive learning experience for the participants.
As the initial outcome of the training was participants' increased confidence and knowledge. Success stories emerged, such as the establishment of a treatment center in Rukum East and the initiation of treatment at Chisapani Hospital, Bardaghat Nawaparasi, previously hindered due to the lack of trained healthcare workers.
Reflecting on the training, several key lessons emerged.
- Preparation is Key: Thorough preparation before the training significantly contributes to its success, ensuring seamless delivery of content.
- Practical Training Enhances Learning: Hands-on practical sessions proved to be invaluable, enhancing participants' understanding and skills in snakebite management.
- Tailored Learning Materials: Developing educational materials in the local language enhances comprehension and engagement among participants.
Looking ahead, it is essential to continue such training initiatives, emphasizing practical learning and strengthening the network of trained healthcare providers across Nepal. By empowering these heroes on the frontlines, we can collectively combat the menace of snakebites, saving lives and fostering a healthier future for Nepal. Together, we can transform challenges into opportunities and create a safer environment for all.